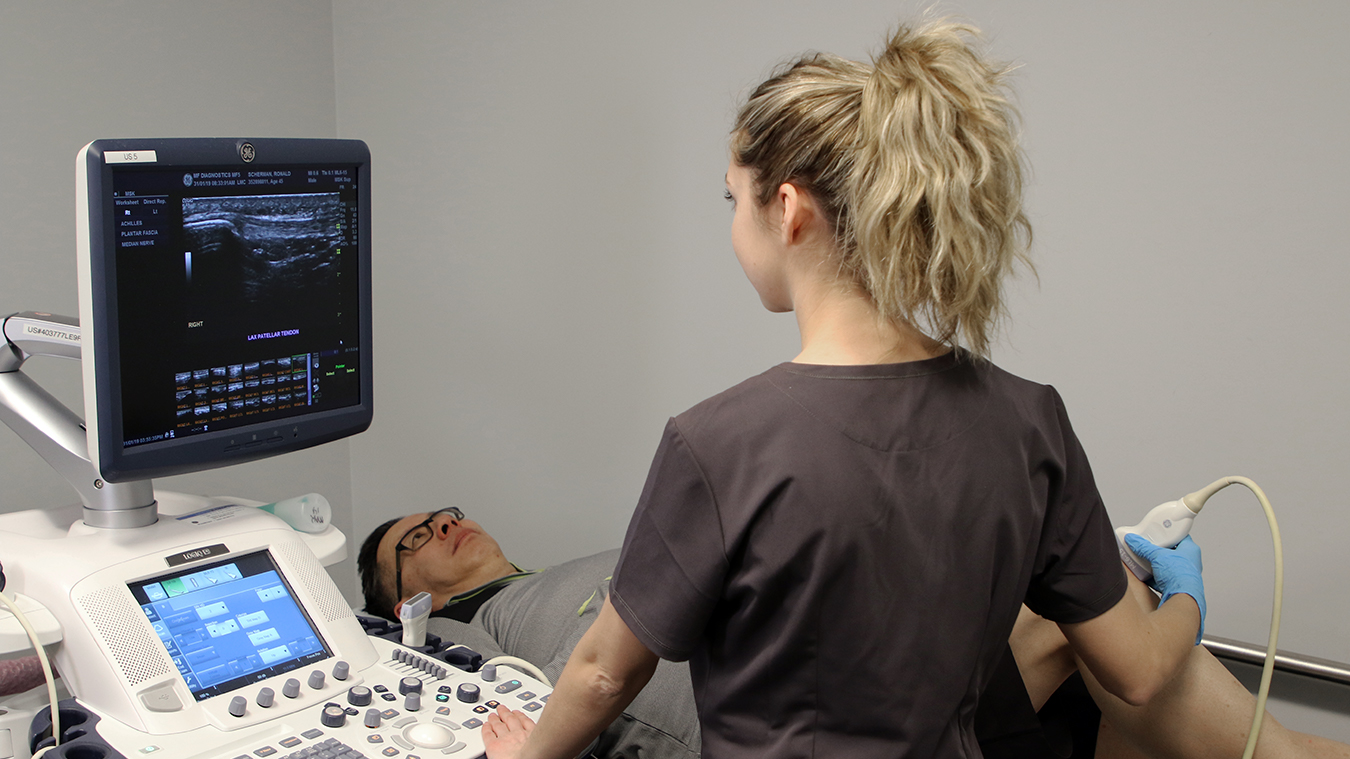
Ultrasound technology, often referred to as sonography, is a widely used medical imaging tool that has revolutionized healthcare. It is a non-invasive, safe, and versatile method for visualizing internal structures of the body. In this article, we will explore the fundamentals of ultrasound technology, how it works, and its diverse applications in the medical field.
How Ultrasound Works:
Ultrasound imaging utilizes high-frequency sound waves, typically inaudible to the human ear, to create detailed images of the body’s internal structures. The basic principles of ultrasound involve the following steps:
Transducer: An ultrasound machine includes a handheld device called a transducer. It emits sound waves and records the echoes as they bounce back.
Sound Waves: The transducer sends out sound waves that penetrate the body. These waves encounter various tissues and structures within the body.
Echoes: When sound waves encounter a boundary between different tissues or structures, some of the waves are reflected back to the transducer as echoes.
Image Formation: The ultrasound machine processes the echoes and converts them into a real-time visual image. This image is displayed on a monitor and can be recorded for further analysis.
Applications of Ultrasound Technology:
Ultrasound technology has a broad range of applications in healthcare, including:
Obstetrics: Ultrasound is commonly used for monitoring the development of a fetus during pregnancy. It provides crucial information about the baby’s health and growth.
Cardiology: Cardiologists use ultrasound to visualize the heart and its structures. This is known as echocardiography and helps diagnose heart conditions.
Abdominal Imaging: Ultrasound is used to examine the liver, kidneys, pancreas, and other abdominal organs. It can detect issues such as gallstones or liver disease.
Musculoskeletal Imaging: Ultrasound helps assess musculoskeletal conditions, such as tendon or ligament injuries.
Breast Imaging: Breast ultrasound is a valuable tool for detecting breast abnormalities and assessing breast health.
Vascular Studies: Vascular ultrasound is used to assess blood flow and detect blockages or abnormalities in blood vessels.
Benefits of Ultrasound:
Safety: Ultrasound imaging does not involve ionizing radiation, making it safe for repeated use, including during pregnancy.
Non-Invasive: It does not require surgical procedures, which can be invasive and carry risks.
Real-Time Imaging: Ultrasound provides real-time images, allowing healthcare providers to observe the body’s functioning as it happens.
Versatility: Ultrasound can be used in various medical specialties and for different types of imaging, including 2D, 3D, and Doppler ultrasound.
Ultrasound technology is a remarkable medical imaging tool that has transformed healthcare by providing non-invasive, safe, and versatile imaging options. From monitoring pregnancies to diagnosing cardiac conditions and assessing abdominal organs, ultrasound plays a pivotal role in patient care. Its ability to deliver real-time images without exposure to ionizing radiation makes it an invaluable asset in the medical field, contributing to early diagnosis and improved patient outcomes.